2022-12-23BY Immikorea

The E7 visa is the most representative visa that allows Korean companies to hire foreign professionals. The company’s main business and the foreigner’s education, major, and career must match well, and the need for employment is well explained through a written statement of employment is the key to issuing an E7 visa.
There are various reasons why an E7 visa may be denied.
First, the most representative reason is because of the wrong choice of occupation.
Although the business environment is highly developed and the skills and abilities of professional manpower required by companies are diverse, the current E7 visa regulations include only a limited number of occupations, including 67 professional occupation, 9 semi-professional occupations, and 6 general skilled occupations. are meant to be selected.
For this reason, it is difficult for companies in industries where it is difficult to clearly distinguish the boundaries of work, where foreigners are hired to do this and that, and it is difficult to select the correct type of job. is often missed.
Second, it is a case where the reason for statement employment is not well written.
A statement of reason for employment should appeal to the visa officer for the company’s capabilities and vision and convince them of the necessity of hiring foreigners. It’s not easy.
Large or publicly traded companies can claim the need to hire foreigners on their own, but small start-ups with little or no track record are subject to stricter visa screening criteria. Therefore, it is important to write a reason for employment that can be contextual and show that the small company has a vision.
Third, if you do not meet the basic qualifications.
Even if you choose the wrong occupation or the reason for employment is insufficient, you can modify and submit it, but if the basic qualifications are not met even slightly, permission will be rejected immediately.
Basic qualifications include both the foreigner who is the target of employment and the qualifications of the company seeking employment. Since basic qualifications may vary depending on the type of job you choose, you should proceed with visa issuance after checking from the beginning.
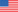
Education and Career
- Hold a master’s degree in a field related to the job opening
- Hold a bachelor’s degree in a field related to the introduced occupation + 1 year or more of experience in the field
- More than 5 years of work experience in a field related to the job to be introduced
Special Qualifications (education and experience waivers for employment necessity)
- One year or more of professional work experience at one of the world’s top 500 companies
- Graduated from world-class universities (planned) Bachelor’s degree holders (Universities within the top 500 QS world universities)
- Graduates (planned) from domestic vocational colleges-Exemption from career requirements when working in a major-related industry
- Bachelor’s degree from a domestic university (expected) – any major, no experience required
- Those who graduated with work-study-linked study (D-2-7) qualification are exempt from applying the national employment rate
- Outstanding talent in cutting-edge science and technology, recommended by KOTRA, Small and Medium Business Corporation
- If you are a high-tech intern on a D-10-3 visa for more than one year and your wages are equal to or greater than the previous year’s GNI.
- Have an employment recommendation from a government ministry and earn an annual compensation of at least 1.5 times GNI.
- Highly compensated professional talent: Annual compensation of more than 3 times GNI (no employment reference required)
- Excellent Private Institution Training Completion
1. In principle, companies with fewer than 5 national employees and a focus on domestic demand are limited.
When issuing an E7 visa, it is often misunderstood that there must be at least 5 Korean employees working in the company. However, only a few occupations, including overseas sales, are applicable, and there are many occupations that can be issued even if there are only 2 or 3 employees.
2. Restriction on the employment rate of foreigners
In principle, foreigners are allowed to be hired within 20% of national employees.
Proof of Korean employment refers to the number of persons who have been registered for more than 3 months who meet the minimum wage in the employment insurance subscriber list. Even if it is a newly established company, it is a rule to apply after 3 months from the date of registration for businesses to which the rate of Korean employment applies.
However, if there is a recommendation from the competent ministry (KOTRA, Korea International Trade Association), etc., additional employment is permitted within the range of 50% of the total national workers in the high-tech industry and within the range of 70% for excellent exporters targeting special language regions. If there is a criterion, apply that criterion
3. Must meet minimum wage requirements
- Professional manpower: 80% or more of the previous year’s GNI paid
- Paraprofessional and below: Pay at least minimum wage
- Small, venture, and nonmetropolitan middle market businesses exception: 70% or more of GNI
- Employee has not worked for a domestic company for 3 years or less.
- Submit small business (SMB) verification / venture business verification / mid-sized business verification
4. Employer must not have arrears of tax (national tax, local tax)
Employment recommendation letters for central government ministries are not required to be submitted in all occupations, and the mandatory submission of occupations is separately determined (16 occupations).
In practice, most cases proceed without receiving a recommendation letter for employment, but there are cases in which a person to be hired deliberately receives and proceeds depending on various special circumstances (?).
The statement for employment (application plan) must be submitted in all industries.


1. In case the applicant for the E7 visa is overseas
- – Prepare visa documents and apply for a visa issuance certificate to the immigration office having jurisdiction over the company address
- – If permission is granted, the confirmation of visa issuance will be emailed to the foreigner
- – For foreigners, submit it to the Korean consulate in the country
- -Enter Korea after visa issuance is completed
- – Apply for alien registration card within 90 days
2. In case the applicant for the E7 visa is in Korea
- – Prepare visa documents and apply for change of status of stay and alien registration card at the Immigration Office having jurisdiction over the company address
- – Receive alien registration card upon approval
3. Issuance time
- – After submitting E7 visa documents to the Immigration Office, it takes approximately 3-4 weeks to review whether or not to approve them.
- – This includes the time required to have foreign documents such as diplomas and work experience certificates notarized by an apostille or consulate.
- – In the case of small businesses, it may take additional time to go out on-site due diligence.
E7 visa holders can invite their spouses and children to F3 visas for stable work life. The length of stay is the same as that of the main resident.
You can apply for the E7 visa at the same time and enter the country together, or you can apply at a later time.
F3 visa is impossible to work, and may be partially available in limited occupations such as English conversation instructors. If your spouse is eligible for an E7 visa, you can change your visa status.
Companies can hire job seekers (D-10 visa) holders as interns. You can work as an intern for up to 6 months, and you can change to an E7 visa midway. However, it is not possible to change to an E7 visa unconditionally, and even in this case, the conditions of the E7 visa must be met.
E7 visa holders can change their place of work. For example, if you are moving from the head office to a branch, you can report it to the immigration office within 14 days.
If you are moving to another company, you cannot change your job without the consent of your original employer, unless there are unavoidable circumstances such as suspension or closure of the company you are working for, or delayed payment of wages. You will need a change of employment agreement from your original employer.
Depending on your industry, you may need to file after you change jobs, or you may need to get clearance before you change jobs.
- Integrated application
- Employment letters
- Documents related to establishment of employment organization
- Employment contract
- Documents proving company sales performance
- Tax payment certificate
- Details of Employment Insurance Insured Persons
- Employment recommendation letter (if necessary)
- Bond (if required)
- Documents separately determined for each job type
- Documents proving foreigner qualification requirements
- Diploma
- Certificate of experience
- Certificates, etc.
- Marriage certificate for family invitation Family certificate
Additional documents may be added or subtracted because the documents to be submitted are different by company and job type
There are many cases where the industry you want to hire is not listed in the occupational code, or you have to select a similar occupation and apply for an E7 visa. If the code is incorrectly applied, not only will you be disapproved, but if you re-apply for the same target and match the same company again, the likelihood of issuing a visa will be very low. So, you need to make good code choices in the first place. This is very important
| Visa | Classification | Occupation |
| E-7-1 | Professional manpower | Managers and Experts (67 Occupations) |
| E-7-2 | Associate-professional manpower | Office and service workers (9 occupations) |
| E-7-3 | General Skilled Labor | Skilled Trades and Allied Workers (8 occupations) |
| E-7-4 | Skilled skilled manpower (score system) | E-9 occupations (3 occupations) |
| E-7-91 | FTA independent expert |
Click to view job-specific requirements and issuance examples
end . manager : 15 Dog occupation => E-7-1 1) Senior executives of economic interest groups (S110) 2) Senior corporate executives (1120) 3) Management support manager (1212 舊1202) 5) Insurance and financial manager (1320) 6) Culture, art, design and video manager (1340) 7) Information and communication related manager (1350) 8) Other professional service manager (1390) 9) Construction and mining related manager (1411) 10) Product production manager (1413) 11) Managers related to agriculture, forestry, livestock, and fisheries (14901) 12) Sales and sales manager (1511) 13) Transportation related manager (1512) 14) Managers related to accommodation, travel, entertainment and sports (1521) |
I . Experts and related workers : 52 Dog occupation => E-7-1 2) Natural science expert (2112) 3) Research Institute of Social Sciences (2122) 4) Computer Hardware Technician (2211) 5) Communication Engineering Technician (2212) 6) Computer system design and analyst (2221) 7) System software developer (2222) 8) Application software developer (2223) 11) Network system developer (2232 舊2225) 12) Information Security Specialist (2233 舊2226) 14) Architectural engineering engineer (2312-newly established) 15) Civil engineering expert (2313 舊2312) 16) Landscape Engineer (2314 舊2313) 17) Urban and transportation experts (2315 舊2314) 18) Chemical Engineering Technician (2321) 19) Metal/Material Engineering Technician (2331) 20) Electrical Engineering Engineer (2341 舊2351) 21) Electronic Engineering Technician (2342 舊2352) 22) Mechanical engineering engineer (2351 舊2353) 23) Plant Engineering Engineer (23512 舊23532) 24) Robotics Expert (2352) 25) Automobile·Shipbuilding·Airplane·Railway Vehicle Engineering Expert (S2353) 26) Occupational Safety and Risk Expert (2364) 27) Environmental Engineering Engineer (2371 舊2341) 28) Gas and Energy Engineer (2372 舊9233) 29) Textile Engineering Technician (2392) 30) History of Drafting (2395 舊2396) 31) Nurse(2430) 32) University Lecturer (2512) 33) Technical Instructor at Overseas Technical College (2543) 34) Education-related experts (2 5 91) 35) Teachers at foreign schools, foreign educational institutions, international schools, and gifted schools (2599) 37) Government and Public Administration Specialist (2620) 38) Special agency administrative personnel (S2620) 39) Management and diagnosis expert (2715) 40) Finance and Insurance Specialist (272) 41) Product Planning Expert (2731) 42) Travel Product Developer (2732) 43) Advertising and PR Specialist (2733) 44) Research Specialist (2734) 45) Event planner (2735) 46) Overseas Salesperson (2742) 47) Technical Salesperson (2743) 48) Technology management expert (S2743) 49) Translator/Interpreter (2814) 50) Announcer (28331) 52) Video related designer (S2855) |
end . Office worker : 5 Occupation => E-7-2 1) Duty free shop or sales clerk in Jeju English Education City (31215) 2) Air transport clerk (31264) 3) Hotel receptionist clerk (3922) 4) Medical Coordinator (S3922) 5) Customer consultation clerk (3991) |
I . Service worker : 4 Dog occupation => E-7-2 1) Transportation service worker (431) 2) Tourist interpreter guide (43213) 3) Casino Dealer (43291) |
.. General Skilled Labor . 8Occupations => E-7-3 1) Animal breeder (61395) 2) Aquaculture engineer (6301) 3) Halal slaughterhouse (7103) 4) Musical instrument manufacturer and tuner (7303) 5) Shipbuilding welder (7430) 6) Aircraft maintenance personnel (7521) 7) Ship Electricity Source (76212) 8) Ship Painter (78369) |
我. Skilled Workforce Score system 3Occupations => E-7-4 (click) 1) Skilled craftsman of root industry company (S740) 2) Agriculture, forestry, livestock and fishery skilled craftsman (S610) 3) General manufacturer and construction company skilled craftsman (S700) |
The above may change in part due to immigration policies
When E7 visa is not granted 100% Refund
The Imi Korea Administrative Office has a lot of experience in relation to the E7 visa, and based on this, we provide accurate consultation on the possibility of issuing the E7 visa through a preliminary review.
So far, we have had a 100% success rate in issuing visas, and there have been cases where we have been granted permission after re-applying for cases that were previously rejected. With this confidence, we are implementing a 100% money-back guarantee system in case a visa is not granted.
Please send us the pre-review materials below and we will review them right away.
Change from E-7-4 visa to F-2-99 visa
E-7-4 change to F-2-99 F-2-99 application for E-7-4 visa holders If you have been in the E-7-4 status for more than 5 years, you can